Doctors treating patients with traumatic brain injuries (TBI) face an arduous task. They must determine the severity of the injury, which will affect treatment plans.
Observation and traditional clinical tests such as CT scans and MRIs are the most common method of assessing TBIs. This method has been demonstrated to be effective for mild TBIs but does not work well for moderate or severe cases.
And with traumatic brain injuries being one of the leading causes of death and disability, it is vital to have better ways of assessing injuries.
Fortunately, new research has found a way to accurately diagnose moderate to severe traumatic brain injuries. The new method measures the percent change in pupil size in response to light. This method is effective in diagnosing moderate and severe TBIs.
Measuring the percent change in pupil size and pupil dilation velocity provides a more accurate reading of the severity of a brain injury than other methods.
This article will discuss the science behind measuring pupil dilation, how it can help diagnose TBIs, and what this means for the future of neurology and traumatic injury treatment.
What is traumatic brain injury?
Traumatic brain injury (TBI) is brain damage caused by an outside force. TBIs can be mild, moderate, or severe. They are often caused by motor vehicle accidents, falls, and sports injuries.
In mild TBIs, people are usually conscious of their surroundings. They may have a headache, dizziness, or memory problems. In moderate TBIs, people often lose consciousness for at least five minutes. They may also be confused about what happened before, during, or after the injury.
Severe traumatic brain injuries are the most severe. They often result in a coma or the inability to wake up. People may have brain bleeding or damage to their brainstems, which control breathing and heart rate.
What is pupil evaluation?
When a patient suffers a traumatic brain injury, they usually cannot help the doctors determine the severity of their injuries. The pupils, however, can provide clues about how bad a person’s brain injury is.
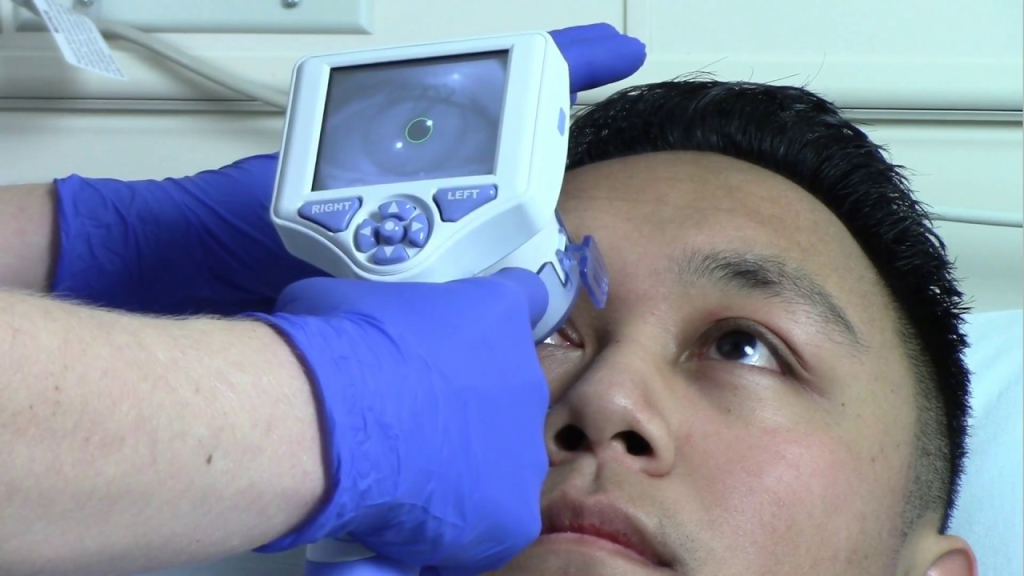
Pupil evaluation is checking the size and responsiveness of a person’s pupils. It is performed by shining a light in each eye and watching how they react. A neurologist may also use a pupilometer to measure the size of a person’s pupils. This can help them determine if there is any damage to their brains and what kind of treatment they need.
What is Pupil Dilation Velocity?
Pupil dilation velocity is the speed at which a person’s pupils dilate when exposed to light. It is used as a measure of the neurological pupil index and indicates brain injury severity.
A person with a head injury may have a slower pupil dilation velocity than someone with no damage to their brain. The doctor will compare the results with those of other tests, such as a CT scan or MRI, to determine if any brain damage is present.
This test effectively diagnoses traumatic brain injury, concussion, and other types of head trauma. Doctors can also use it to monitor the progression of a person’s recovery from an injury.
The Importance of Pupil Dilation Velocity in Pupil Evaluation
Doctors can learn much about a person’s condition by examining their pupils. They’ll look at the size and shape of the patient’s pupils and how quickly they react to light.
If there is any damage to the brain, it will probably be reflected in the patient’s pupil dilation velocity (PDV).
Why is the pupilometer popular among doctors to assess pupil dilation?
The pupilometer is a handheld machine that can quickly and objectively test the size of someone’s pupils. It uses light to gauge how quickly they react to changes in brightness, helping doctors determine whether or not there has been any damage to the brain.
The device is prevalent among optometrists, neurologists, and people who work in critical care settings. It is a quick and easy way to assess someone’s pupil response objectively.
Benefits of using the pupilometer in pupil evaluation
There are many benefits to using a pupilometer in pupil evaluation.
Improved Quality of Neurological Exam
The first reason doctors love the pupilometer is that it improves the quality of their neurological exams.
By quickly and accurately testing a patient’s pupils, they can get more information about what is going on inside the brain. This can help them make better diagnoses and provide better patient treatment options.
Adherence to Hospital Protocols
In many hospitals, there are strict protocols for how to perform a neurological exam. These protocols often include testing pupil response as one of the first steps in diagnosis.
By using a pupilometer, doctors can ensure that they follow the proper protocol and do not miss any vital information about their patient’s condition.
Reduction in Manual Entry Errors
Human errors are a major cause of medical errors. When doctors manually enter data into an electronic system, they are more likely to make mistakes when tired or rushed.
By using a pupilometer, doctors can reduce the number of manual entry errors in their patient records and make sure that all information is accurate. This can also help them reduce the time to complete their neurological exams.
Cost and Time Savings in Medical Care
Using a pupilometer can also help doctors reduce their medical costs by reducing the time spent on each patient. Doctors can complete their neurological exams more quickly, which means they can see more patients in a day or week.